2023. 4. 16. 00:38ㆍ_Study/Network
Network Models 🐇¸.•*¨*•¸.•*¨*•¸.•*¨*•¸.•*¨*•
참고 자료 : 데이터 통신과 네트워킹 4판
#0415 데이터통신 #컴퓨터망 #네트워크프로그래밍 #종합설계프로젝트
해당 자료는 강의 학습자료입니다. 강의 이외의 내용은 검색 및 다양한 자료를 통해 공부하며 정리한 내용의 포스팅입니다.
1. Protocol Layering
2. TCP/IP Protocol suite
3. OSI Model 7계층
용어 정리
Protocol (통신 규약)
Protocol Layering (프로토콜 계층화)
Hop : host, router
Hop to Hop delivery
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
International Organization for Standardization : ISO
Open System Interconnection : OSI
1. Protocol Layering
A protocol defines the rules that both the sender and receiver and all intermediate devices need to follow to be able to communicate effectively.
When communication is simple, we may need only one simple protocol.
when the communication is complex, we need a protocol at each layer, or protocol layering.
프로토콜은 송신자와 수신자사이의 모든 중간 장치가 효과적을 통신하기 위해서 따라야하는 규칙을 정의한다.
소통이 간단할때, 하나의 프로토콜이 필요할지도 모르지만, 복잡해지면 각 계층마다 프로토콜, 즉 프로토콜 계층화가 필요하다.
Simple-layer Protocol : 한 개의 계층으로 충분

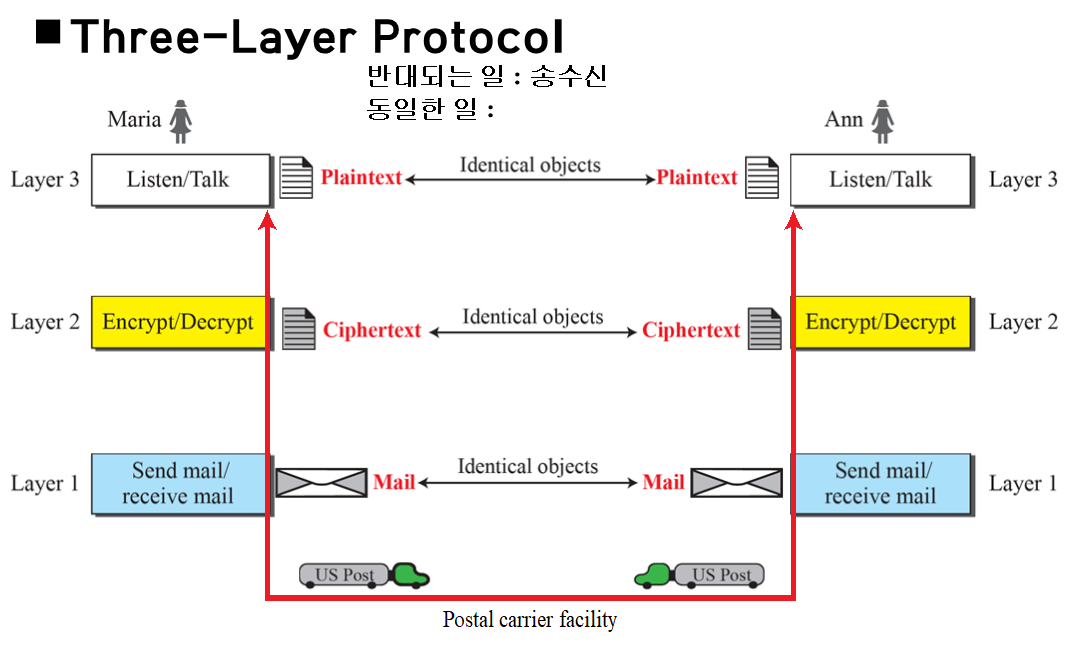
The mails are translated using encryption or decryption technique.
메일은 암호화 또는 복호화 기술을 사용하여 번역 된다.
Two principles of protocol layering.
1. Each layer is able to perform two opposite tasks in bidirectional communication.
-> listen/speak, Give/Take, Send/Receive
2. The two objects under each layer at both sites should be indentical.
-> Plain text letter, Cipher text, Envelopend mail.
각 계층은 양방향 통신에서 두 가지 상반된 작업을 수행할 것.
두 사이트의 각 층 아래에 있는 두 객체는 동일할 것.
Logical connection between peer layers means layer-to-layer communication. 계층 간 통신
2. TCP/IP Protocol suite
Layers in the TCP/IP protocol suite(한 벌, 한 줄, 한 조)

Communication between two hosts.
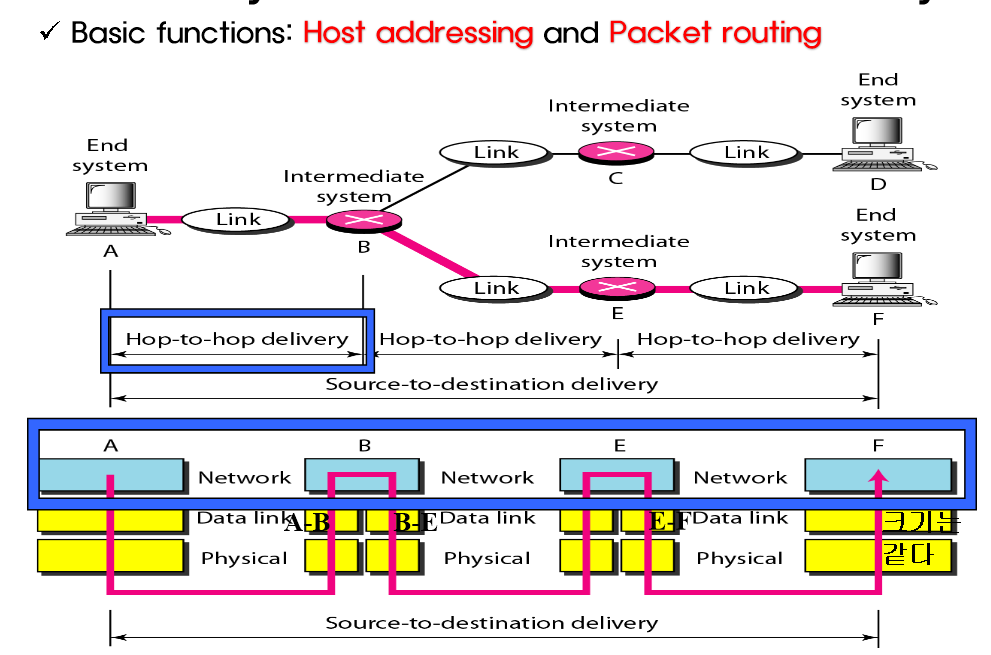
- We assume a small internet made up of three LANs. with connected by one router.
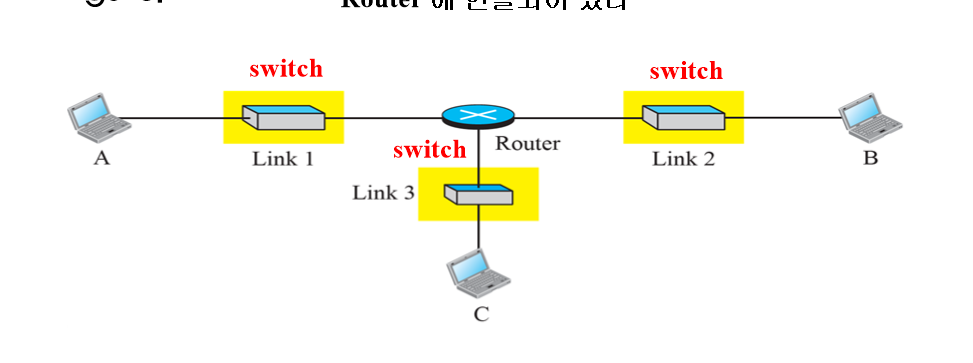
- Source and destination hosts are invloved in all five layer. : 송신자와 수신자는 5개의 계층
- Two link layer Switch is involved in two layers. : 스위치는 2층만
- The Router is involved in three layers. : 라우터는 3층만, 논리연결이 끊어진다.
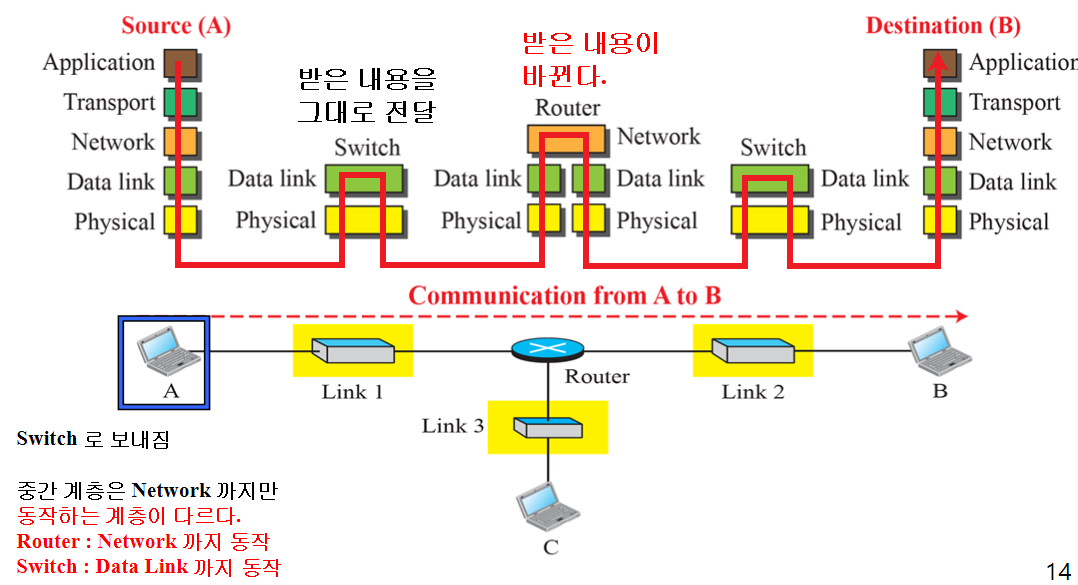
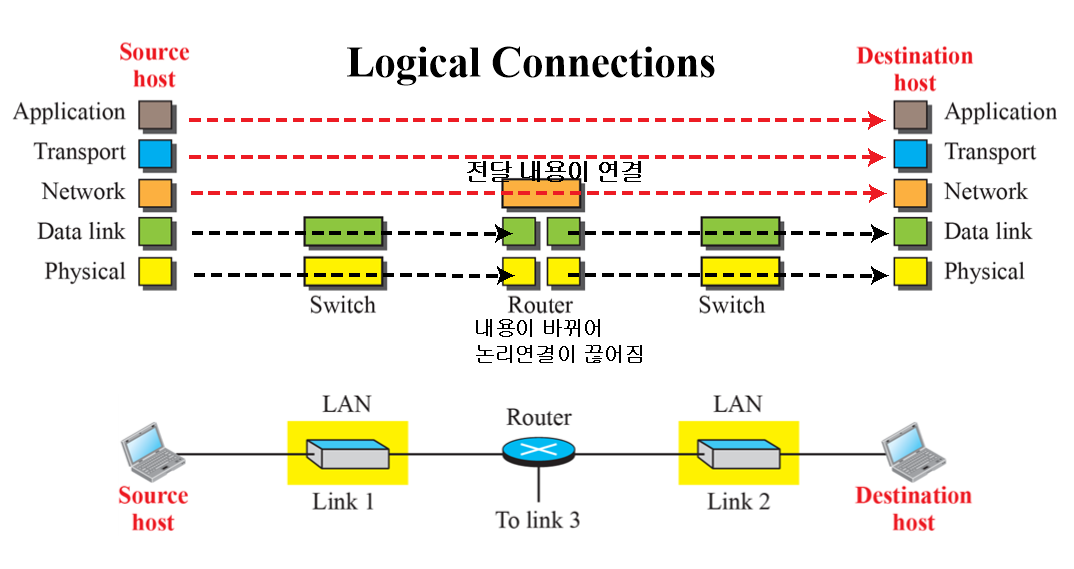
내용이 바뀌면 논리 연결이 끊어진다고 말한다. 이때 header에 link layer주소가 바뀌기 때문에 내용이 같지 않다고 한다. 자세한건 뒤에 나오는데 IP주소를 통해 목적지에 도달하게 되는데. 복잡한 네트워크에선 바로 도착할 수 없고, 다음 노드의 link layer주소만 필요하다. 따라서 header에 link layer주소를 계속 변경해서 넣어주면서 (IP주소(최종도착지)는 동일하다) Frame 내용이 바뀌게 된다. Frame은 Network층에서 내려온 datagram 여기다가 다음 목적지MAC,송신측MAC,타입, 오류확인 등등 붙이다보면 Frame이 되며 이를 Data link 층이 옮긴다. 그러니까 Router입장에선 아래 계층의 내용이 동일해야하는데 패킷의 내용이 바뀐 것이므로 논리적인 연결이 끊어지게 된다. 라우터는 data link 계층에서 매번 새로운 frame을 만들어 전달해야한다.
The functions and duties of layers in the TCP/TP
- The functions and duties of application, transport and network layer are between end-to-end.
The functions and duties of datalink and physical layer are between hop-to-hop:
Hop : 한 발짝
스위치는 한 홉이 아니다. (전달만 해줌)
Host(computer) or Router is considered one hop.
Identical objects in the TCP/TP protocol

| layer | Identical objects | Basic function |
| Application | messages | |
| Transport | segment, user datagram | Error&Flow & congestion Control Process to process delevery |
| Network | datagram | Host addressing Packet routing |
| Data link | frame | Framing Node to node (hop to hop) delivery Error control |
| Physical | bits |
하나씩 알아보자.
Physical Layer : 물리계층, bits
Physical layer is responsible for the movemets of individual bits form one hop (node) to the next.
This layer consists of the electronic circuit transmission technologies of a network.
물리 계층은 개별 비트가 한 홉에서 다른 홉으로 이동하는 것을 담당하고.
이 계층은 네트워크의 전자 회로 전송 기술로 구성된다.

Data link : 데이터링크 계층 , frames
Data-link layer is responsibie for moving frames from one hop(node) to the next hop.
Frame is the data unit in data-link layer.
Basic functions : Framing, Node-to-node(hop to hop) Delivery, Error control.
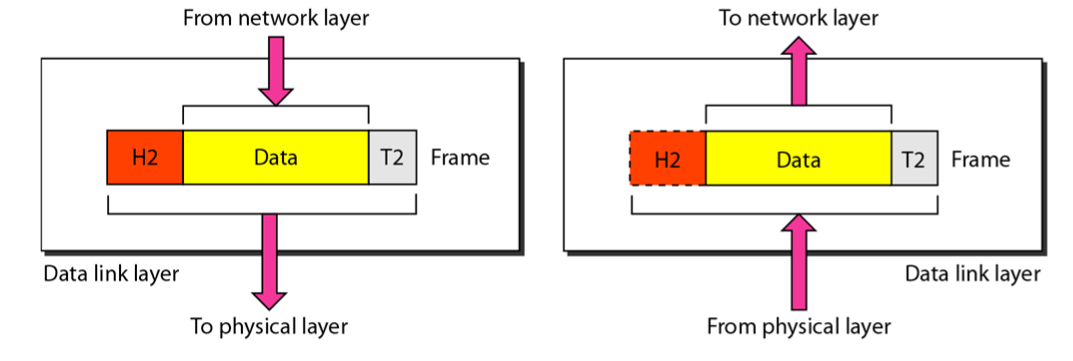
Hop to Hop delivery
- Data link layer transfers frame(data) between adjacent(이웃) nodes or between nodes.

Network layer : 네트워크 계층, Packets, 송신측 -> 수신측 error 없이 전달
The network layer is responsible for the delivery of individual packets from source to destinaion host.
Host to Host delivery.
Basic function : Host addressing, Packet routing
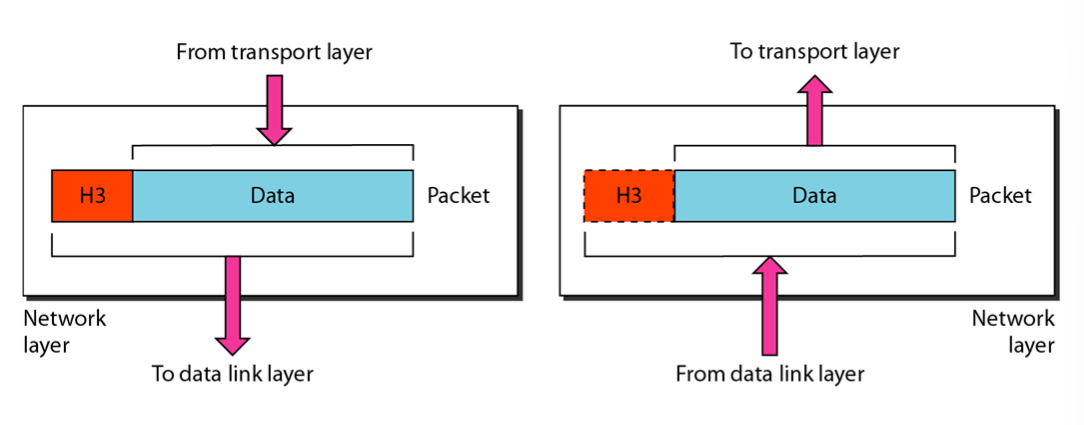
Transport Layer : 전송계층 , channel, segment, user datagram
Transport layer provides process-specific transmission channels for applications.
Port to Port Delivery : 프로세스 to 프로세스

the transport layer is responsible for the delivery of a message from one process to another.
Basic function: Error & Flow & Congestion Control, Process to process delivery.

Application Layer : 응용 계층 , message
the application layer is responsible for providing services to the user.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
- the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
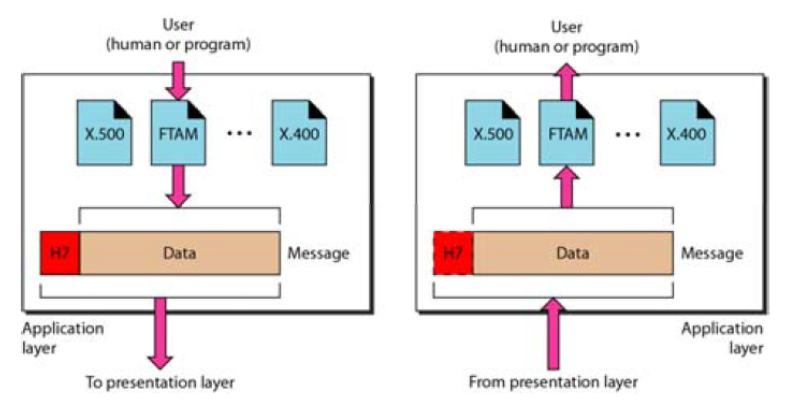
Encapsulation and Decapsulation
The important concepts in protocol layering
- Encapsulation at the source host
- Decapsulation and Encapsulation at the router.
- Decapsulation at the destination host.
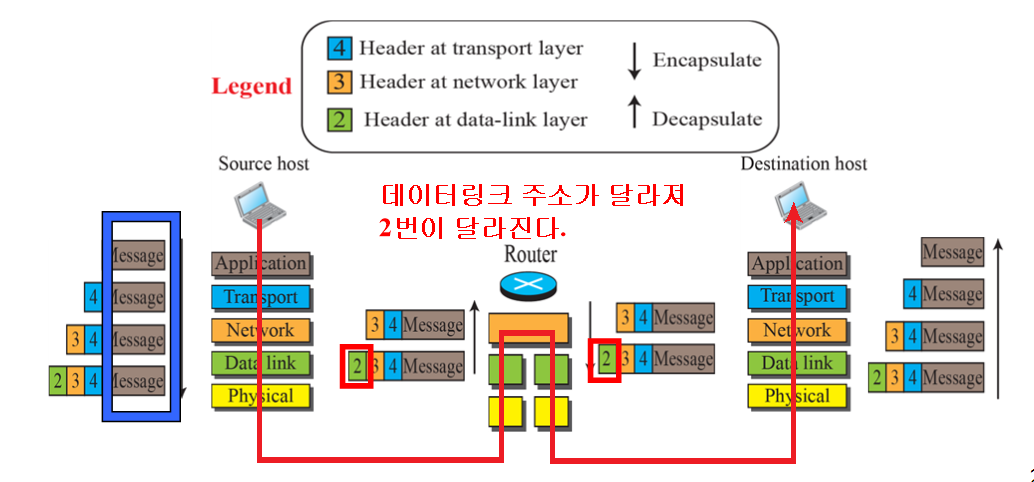
이때 앞서 말했듯, 라우터에선 2번 header 부분이 달라진다.
Addressing
There exists logical communicaion between pairs of layers.
Any communication needs two addresses: source, destination address
- physical layer does not need addresses.
- the unit of data at the physical layer is as bit, which cannot have an address.

Link-layer Address : 데이터 링크 계층 frame
- locally defined addresses. 로컬로 정의된 주소.
- They defines a specific host or router in a LAN or WAN
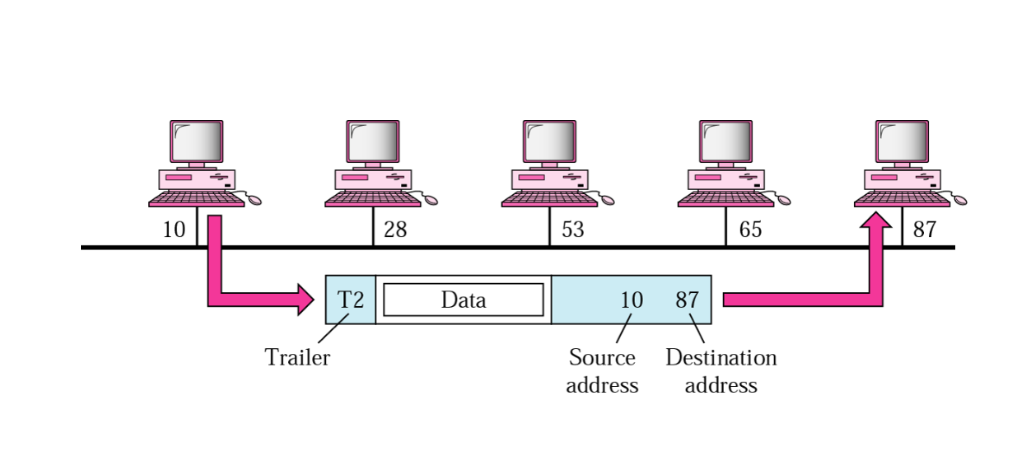
Network layer Addresses : Logical Address
- The addresses are global, with the whole internet as the scope
- 32-bit IP addresses are network layer addresses

Transport layer address : Port Number
- Port numbers are local addresses that distinguish between several programs running at the same time.
포트 번호는 동시에 실행되는 여러 프로그램을 구분하는 로컬주소이다.

Application layer address : Names (Specific address)
- Email address, Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
3. OSI Model 7계층 : 물데네전세표응
International Organization for Standardization : ISO conducted a program to develop general standards and methods of networking.
Open Systems Interconnection(OSI) is abstract model of networking.
- OSI promoted the idea of protocol layering. defining interoperability between network devices and software.
- ISO organization , OSI model , Organization이 기관인데. 상식적으로 기관이 먼저 나오진 않는다고 생각하자. Open임.

the OSI model appeard after the TCP/TP protocol suite. - TCP/IP가 먼저 개발
OSI model did not replace TCP/TP reasons (3)
- OSI was completed when TCP/TP was fully in place.
- Some layers (Session and Presentation layer ) in the OSI were never fully defined.
- OSI did not show high enough level of perfomance to switch from TCP/TP to OSI model
- OSI는 TCP/IP의 기능이 훌륭했기 때문에 완전히 대체하지 못했다.
- OSI 일부 계층 (세션, 표현계층)은 별로 할 일이 없었다.
- OSI는 TCP/TP 모델에서 OSI모델로 전환하기에 충분하고 뛰어난 성능을 보여주지 않았다.
따라서 자주 사용하는 TCP/TP를 사용하지 굳이 바꿀 필요가 없었다.
'_Study > Network' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴퓨터망] Introduction to physical layer (0) | 2023.04.17 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터망] Data comuunications (1) | 2023.04.15 |
| [컴퓨터망] Media Access Control(MAC) (0) | 2023.04.06 |
| [Network] TCP 기반 서버 / 클라이언트 (0) | 2023.03.31 |
| 네트워크 프로그래밍과 소켓의 이해 #network (0) | 2023.03.30 |